How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to precision inspections. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and navigating legal regulations. We’ll demystify the technology, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone flight controls, delve into camera operation for stunning visuals, and offer practical advice on maintenance and troubleshooting. By the end, you’ll be well-prepared to handle your drone with expertise, capturing incredible footage and enjoying the thrill of aerial flight.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various parts of a drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section details the key components and defines common terms used in drone piloting.
Drone Components
A drone consists of several essential components working in concert. These include:
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust needed for flight. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. Brushless motors are common due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the “brain” of the drone, responsible for processing data from various sensors and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands from the transmitter.
- Battery: Provides the power to run the motors and onboard electronics. Battery capacity is measured in milliampere-hours (mAh), and higher mAh values typically mean longer flight times.
- GPS Module: Enables the drone to determine its location and altitude, crucial for features like GPS hold and return-to-home.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, ensuring smooth footage even during flight maneuvers. Three-axis gimbals offer the most stability.
- Camera: Captures photos and videos. Features vary widely, from basic cameras to high-resolution models with advanced settings.
- Transmitter (Remote Controller): Used to control the drone’s movements and camera functions. It wirelessly communicates with the drone’s flight controller.
Drone Terminology
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology will enhance your understanding and improve communication with other drone pilots.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode where the drone maintains a constant altitude, simplifying piloting.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, preventing shaky footage.
- Telemetry: The real-time transmission of data, such as battery level, GPS coordinates, and signal strength, from the drone to the transmitter.
- GPS: Global Positioning System, used for location and navigation.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A safety feature that automatically guides the drone back to its takeoff point.
- Failsafe: Emergency procedures that activate if the drone loses signal or encounters a critical malfunction.
Drone Battery Comparison
| Battery Type | Capacity (mAh) | Flight Time (approx.) | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S 1500mAh | 1500mAh | 15-20 minutes | 150g (approx.) |
| LiPo 4S 2200mAh | 2200mAh | 25-30 minutes | 200g (approx.) |
| LiHV 4S 3000mAh | 3000mAh | 35-40 minutes | 250g (approx.) |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount for safe and responsible drone operation. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and legal repercussions.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which can be readily achieved by consulting resources like this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. From there, practice is key to mastering the skills needed for safe and effective drone operation.
Proper drone operation ensures both your safety and the safety of those around you.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform the following checks:
- Inspect propellers for damage or debris.
- Check battery charge level and ensure it’s properly connected.
- Verify GPS signal strength and satellite acquisition.
- Inspect the drone’s body for any damage.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit).
- Check transmitter battery level.
- Review airspace regulations for the flight area.
Safety Considerations
Prioritize safety throughout the entire flight operation. Key safety considerations include:
- Obstacle Avoidance: Maintain a safe distance from obstacles, including trees, buildings, and power lines.
- Airspace Regulations: Familiarize yourself with and strictly adhere to local airspace restrictions and regulations. Many countries require drone registration and pilot certification.
- Visual Line of Sight (VLOS): Keep the drone within your visual line of sight at all times. Do not fly beyond your ability to see the drone clearly.
- Weather Conditions: Avoid flying in strong winds, rain, or snow. Adverse weather conditions can significantly impact drone stability and control.
- Bystanders: Ensure a safe distance from people and property during operation.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Flowchart
A structured approach to takeoff and landing minimizes risks. The following flowchart illustrates the recommended steps:
[A detailed textual description of a flowchart would be included here. The flowchart would depict the steps: Power on transmitter and drone; check GPS signal; perform pre-flight checks; initiate takeoff; hover; perform flight maneuvers; initiate landing; power down drone and transmitter. Each step would be represented by a box, with arrows indicating the flow of actions.]
Basic Drone Flight Controls: How To Operate A Drone
Understanding the basic flight controls is essential for safe and controlled drone operation. This section provides a step-by-step guide to mastering fundamental maneuvers.
Standard Transmitter Controls
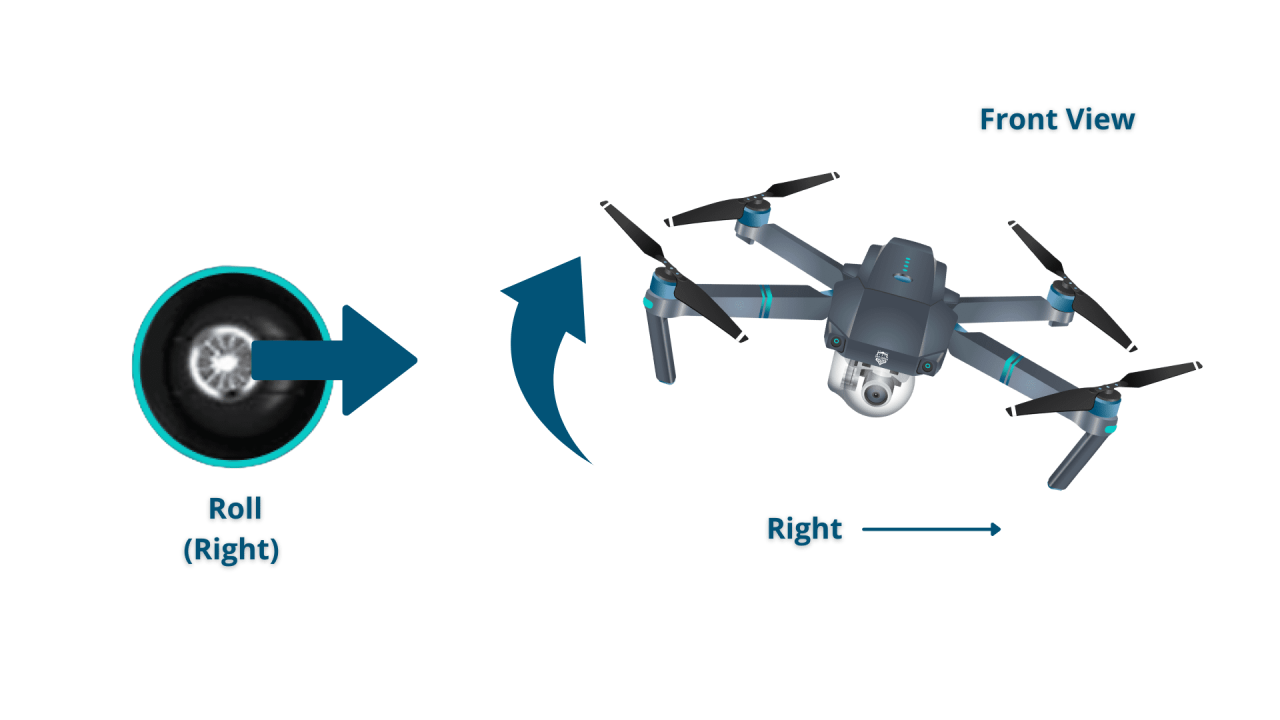
Most drone transmitters use two joysticks. One controls the drone’s pitch (forward/backward) and roll (left/right), while the other controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (altitude).
[A textual description of a typical drone transmitter layout would be included here, detailing the functions of each joystick and button.]
Basic Flight Maneuvers
The following steps guide you through basic drone maneuvers:
- Takeoff: Gently increase throttle to lift the drone vertically.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable position in the air by carefully adjusting throttle and stick inputs.
- Forward/Backward Movement: Gently push the left joystick forward to move the drone forward and backward to move it backward.
- Left/Right Movement: Gently push the left joystick left or right to move the drone laterally.
- Landing: Slowly lower the throttle to gently set the drone down.
Smooth Flight Mode Transitions
[A textual description of a video script demonstrating smooth transitions between different flight modes (e.g., beginner mode to sport mode) would be provided here. The script would include detailed instructions on joystick movements and throttle adjustments needed for each transition.]
Advanced Drone Flight Techniques
Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, you can explore advanced techniques for more dynamic and precise flights. This section covers advanced flight maneuvers and tips for improving your piloting skills.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
Advanced maneuvers require practice and a good understanding of drone dynamics. These include:
- Precise Hovering: Maintaining a perfectly stable position in the air, even in light winds.
- 360-Degree Turns: Executing smooth and controlled rotations.
- Flying in Windy Conditions: Compensating for wind gusts to maintain stability and control.
- Filming Smooth Cinematic Shots: Using advanced flight techniques to create visually appealing footage.
Tips for Improving Piloting Skills
Consistent practice and attention to detail are key to improving your drone piloting skills:
- Practice in Open Areas: Start practicing in a large, open space away from obstacles.
- Start Slow: Begin with basic maneuvers and gradually increase the complexity of your flights.
- Use Simulation Software: Practice in a safe simulated environment before flying outdoors.
- Watch Tutorials: Learn from experienced drone pilots by watching online tutorials and videos.
Flight Mode Comparison
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control:
| Flight Mode | Stability | Responsiveness | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beginner Mode | High | Low | Beginners |
| Sport Mode | Medium | High | Experienced Pilots |
| Manual Mode | Low | Very High | Advanced Pilots |
Drone Camera Operation and Photography/Videography
Many drones are equipped with cameras capable of capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. This section covers camera settings and techniques for creating high-quality content.
Drone Camera Settings and Features
Typical drone cameras offer various settings and features, including:
- ISO: Controls the camera’s sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values are better for bright conditions, while higher values are suitable for low-light situations.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field. A wider aperture (lower f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background.
- White Balance: Adjusts the color temperature of the image to ensure accurate color reproduction.
- Exposure Compensation: Allows you to adjust the overall brightness of the image.
Optimizing Camera Settings
Achieving optimal image quality involves understanding the interplay between ISO, shutter speed, and aperture. Generally, you want to use the lowest ISO possible to minimize noise. Shutter speed should be fast enough to freeze motion, but not so fast that it results in underexposed images. Aperture depends on the desired depth of field.
Photography/Videography Plan

Planning your shots is crucial for creating compelling content. Consider these shot types:
- Aerial Landscapes: Capture wide shots of landscapes from above.
- Close-Ups: Get detailed shots of subjects from a unique perspective.
- Time-lapses: Create dynamic videos by capturing a series of images over time.
- Tracking Shots: Follow a moving subject smoothly.
- Orbital Shots: Circle around a subject, creating a 360-degree view.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for keeping your drone in top condition and preventing costly repairs. This section covers routine maintenance and solutions to common problems.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule will extend the life of your drone:
- Clean the drone body and propellers after each flight.
- Inspect propellers, motors, and other components for damage.
- Check battery health and charge cycles.
- Calibrate the compass and IMU periodically.
- Replace worn parts as needed.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Here’s how to address common issues:
- Low Battery Warnings: Land immediately and recharge the battery.
- GPS Signal Loss: Relocate to an area with a clearer GPS signal, or wait for the signal to reappear.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors for damage and replace if necessary.
- Gimbal Issues: Recalibrate the gimbal or contact the manufacturer for support.
- Flight Controller Problems: Check for firmware updates or contact the manufacturer for support.
Common Drone Issues, Causes, and Solutions
| Issue | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Charge battery, replace battery, check power switch |
| GPS signal lost | Obstructed GPS signal, interference | Move to open area, restart drone |
| Motor malfunction | Motor damage, loose connection | Inspect and replace motor, check connections |
Drone Laws and Regulations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local laws and regulations. This section highlights key legal aspects and resources for further information.
Legal Aspects of Drone Operation
Drone laws vary by country and region. Key considerations include:
- Airspace Restrictions: Many areas restrict drone flights near airports, military bases, and other sensitive locations.
- Registration Requirements: Some jurisdictions require drone registration with relevant authorities.
- Privacy Concerns: Drone operators must respect the privacy of individuals and avoid unauthorized surveillance.
- Operating Limitations: Weight restrictions, altitude limits, and flight time restrictions are common.
Resources for Understanding Drone Regulations
To stay informed about drone laws, consult these resources:
- Your country’s civil aviation authority website.
- Local government websites.
- Drone industry associations.
Consequences of Violating Drone Laws

Violating drone laws can result in significant penalties, including:
- Fines.
- Drone confiscation.
- Legal action.
For example, flying a drone near an airport without proper authorization could lead to significant fines and legal repercussions. Similarly, violating privacy laws by using a drone to record individuals without their consent could result in lawsuits.
Mastering drone operation is a journey of learning and practice. From understanding the fundamentals of pre-flight checks and basic maneuvers to perfecting advanced techniques and adhering to safety regulations, this guide has provided a roadmap for your success. Remember that consistent practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Now, go explore the skies!
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from takeoff to landing, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone This will equip you with the knowledge needed to confidently and safely operate your drone, ensuring both successful flights and responsible drone use.
Detailed FAQs
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring GPS stabilization and simplified controls. Research models with good reviews and consider your budget.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, flight conditions (wind, temperature), and usage (camera operation, flight style). Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal?
Losing GPS signal can lead to erratic flight behavior. Most drones have return-to-home (RTH) functions, but maintaining visual contact is crucial. Practice emergency landings in a safe area.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and procedures.
